Suprapatellar Bursa: Causes, Treatments
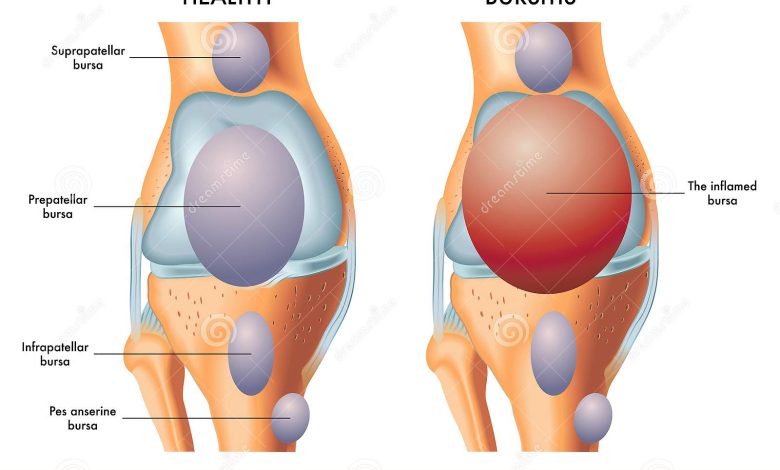
Do you know what bursa is in your body? You can find these are tiny, jelly-like pouches in various parts of the body (like the shoulder, hip, knee, elbow, and heel). These sacs (filled with fluid) lie between bones and soft tissues. Also, these act as a sliding surface to regulate friction. Unfortunately, while these sacs play a significant role in our joint movements, they are susceptible to problems like bursitis. So, this article will highlight a significant ailment – suprapatellar bursa: causes, treatments.
So, you would wonder what suprapatellar is? It is another name for pre-patellar bursitis. It is caused due to swelling of the bursa in your kneecap (patella). So, it happens when your bursa gets irritated or secretes excessive fluid. It leads to inflammation that stresses the adjacent knee parts. So, you are likely to experience pain behind knee, warmth, and sensitivity along with it,
Though bursitis is not infected, the bursa is susceptible to infections. So, if you suffer from non-infectious bursitis, then resting, ice therapy and pain killer can help improve the condition. However, if you have infected bursitis, your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics or surgery.
What is the Cause of Suprapatellar Bursa?
continuous kneeling may trigger suprapatellar bursa as it stresses your internal knee structures. Hence, people whose jobs require them to kneel for long periods are highly susceptible to it. A few examples include electricians, plumbers, roofers, miners, and landscapers.
Besides, a direct hit to your knee can also lead to the development of bursitis. So, players who partake in competitive sports (that involve direct blows or knee falls) like cricket, football, fighting, and basketball are at a higher risk of this ailment. Hence, your bursa may fill with blood due to damage or overuse. A swelled bursa rarely becomes infected with the bacterium diffused through the blood.
However, your risk of developing this condition may elevate if you suffer from rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Usually, crystals deposit within the knee cavity of such patients, which attacks the bursa.
On the other hand, bursitis can also be a cause of bacterial contamination. Sometimes, a wound, insect bite, or scrape can rip your skin apart allowing bacteria to penetrate deeper into the skin, Hence, the infectious particle might enter your bursa sac. Usually, the bacterium staphylococcus (generally found on the skin) attacks the bursa. However, infectious bursitis is not much common, though these are more serious. So, if you suspect you have infectious bursitis, you must immediately visit a specialist, as you should get it treated on a priority basis.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Suprapatellar Bursa?
- You may experience pain when you perform any activity. Though, your nights are peaceful.
- Rapid inflammation on the front side of your kneecap.
- You feel sensitivity and warmth when you touch the knee.
- Septic bursitis may secrete fluid and soreness. You may also experience fever and chills.
What is the Treatment?
If you have bursitis, you can try home remedies, but you must consult a specialist. When you visit a doctor, they will discuss your symptoms. Some of the points of concern include your pain intensity, the duration of your symptoms, and your risk factors. They may also inquire about fever or chills, as septic bursitis requires a specific treatment plan.
Next, the doctor may closely examine your knee and compare its condition to the healthy one. Then, the doctor may use some tools to check the sensitivity of your knee and will evaluate the range of motion of your knee also, whether you feel pain when you flex your knee.
What is the non-surgical treatment?
If you have an inflamed but non-infected bursa, your doctor may recommend a non-surgical treatment. The treatment includes:
Modified Activity
If you have bursitis, you should avoid the activities that aggravate your symptoms. Instead, you should perform more specific and non-impact activities until you fully recover. For example, you should replace your rigorous sports and exercise routines with cycling or walking.
Ice Therapy
You should apply ice packs after every few hours (3-4 times a day) for twenty minutes each time. It will help improve swelling and inflammation. However, it will only be valid if you rest well.
Elevation
You should raise the problematic leg when it is obligatory to walk.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Some commonly used NSAIDs to treat this condition include naproxen and ibuprofen as it helps effectively reduce pain and swelling.
However, if pain and inflammation do not improve through these basic measures, your physician may try “aspiration” to extract your bursa fluid and test it to confirm any infection.
Which Imaging Tests Will the Doctor Suggest for Suprapatellar Bursa?
Further, your doctor may recommend a few imaging tests to picture your knee condition accurately. Some tests include:
X-rays
X-rays provide a clear image of the bones, so it will help whether any fracture is triggering these symptoms.
Computerized Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging Scan
Usually, the suprapatellar bursa is diagnosed through physical examination. However, your doctor may recommend a CT scan or MRI scan to examine your knee for any soft tissue damages.
Aspiration
Your doctor might drain out the bursa if he feels that it is infected. Aspiration is when the doctor extracts fluid from the knee bursa using a syringe and forwards the sample for lab analysis.
Your doctor may drain your bursa with a needle and then inject a corticosteroid into the cavity to treat the condition. This anti-inflammatory drug is more effective than other medications (ingested via mouth). When the bursa is drained, it reduces swelling and improves disability.
Typically, septic bursitis is usually treated through antibiotics. However, if the treatment is not practical, your doctor may proceed with surgery. While after surgery, your knee may regain its movement in a few days while normal activities are resumed within a few weeks.
Physical Therapy
While resting diminishes the metabolic requirement of the damaged tissue, prevents excessive blood flow, and supports the healing process. While ice therapy, compression, and elevation can help improve primary conditions, it is not a proven treatment in clinical trials.
So, after initial swelling has settled, you may proceed with light stretching and muscle strengthening workouts to restore your entire range of motion. Specialized exercises from a physiotherapist help diminish pressure on the tendons and knee joints and support a speedy recovery.





